The complex and highly regulated world of medical device manufacturing has been facing substantial regulatory challenges over the last few years for CE marking in the EU, with an ever changing regulatory landscape triggered by a transition from the Medical Devices Directive (MDD) which has been in place since 1993, to the Medical Device Regulation (2017/745) (MDR) which has been effective since May 26th 2021. The change came into effect to provide consistency for standards around quality and safety across the 27 European Union states. The new regulatory compliance is required by any medical device company or manufacturer who supplies or trades within the European market. The transition was originally extended to May 2024, however due to delays with transition and the risk to supply of medical devices across Europe, proposals have been accepted to further delay this transition deadline to Dec 2027 or even 2028 depending on the risk classification of the device, this is likely still to see a huge bottle neck for the transition of medical manufacturers from MDD to MDR certification despite the timeline extension.
The new regulations apply to all medical device products currently on the market within the EU, which means current products and or devices will be required to undergo MDR review and approval. The MDR is far more stringent than MDD and was enforced with a significant focus around product performance, safety, and Post Market Surveillance (PMS) and whilst not entirely different, there are a significant number of changes that medical device companies will need to adhere to. These changes include updates to the technical documentation and Quality Management Systems (QMS) with a strong focus around evidence. Here are just some of the changes you will see in the MDR:
- The MDR regulation is 4x longer than the MDD regulation and contains 5 more annexes.
- The new law now requires companies to perform global impact assessments.
- Clinical data, safety and performance data, technical documentation and labelling will need to be revised and updated.
- Unique device identification (UDI) will be implemented.
- Quality Assurance, Risk Management and Post Market Expectations will require careful review.
With the new rules in force, bringing a new medical device to market in the EU will need to be in line with MDR regulations, and the importance of a strong regulatory affairs and quality team has never been so apparent. Regulatory affairs and quality control are two critical functions in the medical device industry. Regulatory affairs refer to the process of ensuring that medical devices meet all regulatory requirements set by the government and/or regulatory bodies. The regulatory process involves submitting documentation to regulatory agencies for approval to market to sell medical devices. Regulatory affair professionals must stay up to date with changes in regulations and standards to ensure that medical devices meet regulatory requirements. They are responsible for preparing and submitting regulatory submissions, ensuring compliance with regulations, and keeping records of regulatory activities. A strong regulatory affairs team is essential for ensuring that medical devices meet all relevant regulations, standards, and guidelines, and that they are approved for market. This helps minimize the risk of product recalls, regulatory fines, and legal disputes, and helps to ensure that patients receive safe and effective medical devices.
Quality control, on the other hand, refers to the process of ensuring that medical devices meet the required quality standards. Quality control professionals work to ensure that medical devices meet the necessary safety and performance requirements. This includes designing and implementing quality control procedures, testing devices for safety and effectiveness, and monitoring the production process to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. Quality control professionals are also responsible for investigating and resolving any issues that arise during the production process or after the product is released to the market. A strong quality management system is a critical component of medical device manufacturing, as it helps ensure that medical devices are produced consistently to a high standard of quality. A quality management system (QMS) helps to standardise processes, procedures, and documentation, and provides a framework for continuous improvement and quality control.
Both regulatory affairs and quality control are critical to ensuring that medical devices are safe and effective for use by patients and are essential for any medical device manufacturer. These teams work closely ensuring that medical devices meet the necessary regulatory requirements and quality standards, which ultimately helps to protect patient safety and improve healthcare outcomes.
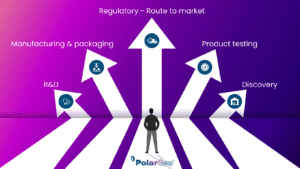
How PolarSeal can help you navigate the ever-changing regulatory landscape to ensure an expedited route to market for medical devices…
- Specialist support on device development for skin contacting devices and prototyping
- Specialist supplier partnerships to ensure state of the art material selection
- Expertise in compliant materials selection (Avoidance of CMR/EDC and rubber and latex)
- Expertise in manufacturability of material combinations to meet safety and performance criteria (GSPR)
- Biocompatibility (ISO 10993-1 )
- Sterilisation (from testing to validation)
- ISO 7 Cleanroom capability
- Performance testing of materials and devices capability
- Packaging and labelling (testing and MDR compliant and UDI requirements)
- Quality System compliant with ISO 13485 and CFR cGMP requirements
- End to end design and development process and output
- Regulatory support services for design control and technical file preparation