Introduction
With a projected CAGR of 15.6% over the next 5 years, wearable medical devices are set to outperform nearly all categories in the medical device market. The growth in this space has created a fiercely competitive environment, attracting a surge of companies from start-ups to established industry leaders hoping to capture a share of the market. To succeed in these conditions, medical device companies need to produce wearables that meet and exceed the demands of consumers for aesthetics, comfort, durability and reliability.
This blog explores the important factors to consider when designing stick-to-skin wearables to ensure your products stand out in an ever more competitive market.
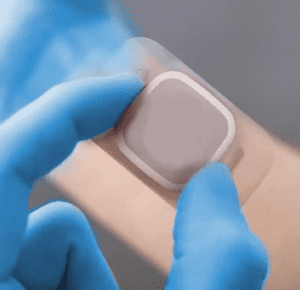
1. Skin Compatibility
Material Selection: To prevent skin irritation and potentially even allergic reactions, biocompatible materials should be used where possible in the device. To this end, hypoallergenic materials should be selected, especially for devices intended for long-term use.
Breathability: It’s also important for the adhesive and materials to allow for skin breathability to avoid moisture build-up.
Adhesive Strength and Longevity: Adhesives must be selected to strike a balance between strength and ease of removal.
2. Comfort
Flexibility: Wearable devices should be designed to conform to the body’s contours, allowing for movement without leading to detachment.
Size and Weight: In general, smaller wearable devices tend to be more comfortable and aesthetically pleasing.
Thermal Comfort: Another very important consideration is how to ensure the device doesn’t become too warm against the skin, which can cause discomfort and reduce adhesive strength.
Application and Removal: Wearables should be designed for easy application and removal by the user.
3. Durability and Environmental Resistance
Water Resistance: To succeed in the competitive wearables market, products must be able to withstand exposure to water from activities like showering, sweating or even swimming. It’s therefore crucial to ensure the device is either waterproof or at least water-resistant by design.
Mechanical Durability: Wearable medical devices should be designed to be able to endure everyday wear and tear, including stretching, bending and friction.
4. Data Accuracy and Reliability
Sensor Placement: Accurate sensor placement is critical for data collection. Wearable medical devices should be designed to maintain their position relative to the part of the body they are monitoring.
Signal Integrity: In addition to sensor placement, it’s also vital that wearable devices are designed such that no materials or components interfere with sensor signals. This ensures reliable data transmission to the monitoring system.
Power Supply: Careful consideration should be given to whether batteries or energy harvesting systems are used as a power supply.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
Manufacturing Costs: Optimizing the design for cost-effective manufacturing processes can help reduce the overall cost of the device, making it more accessible to a wider market.
Longevity and Reusability: Designing for reuse, where appropriate, or ensuring the device’s longevity can improve cost-effectiveness for users.
Why PolarSeal?
As a specialist medical manufacturer, our deep expertise in medical-grade materials, advanced adhesive technologies and ergonomic design principles ensures that your device will stand out in the market, meeting the highest standards of performance, comfort and reliability. Creating a stick-to-skin wearable medical device requires meticulous attention to detail across multiple facets of design and production. By considering these factors early in the design process, you can develop a product that not only meets regulatory standards but also provides a superior user experience.
RELATED CONTENT

From Material to Wearable Reality: PolarSeal®’s CGM Patch Development Explored
The advent of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) patches has revolutionised diabetes management, offering patients a non-intrusive, real-time window into their glucose levels. This technology is
The evolution of the heathcare wearable
The evolution of the wearable medical device traces back to the 13th century with the invention of eyeglasses, by the 1900’s we began to see more

Selecting the optimal wearable adhesive and converting it to perfection
Selecting the correct adhesive for your wearable medical device is crucial to its market success, but with so many adhesives available to the medical market