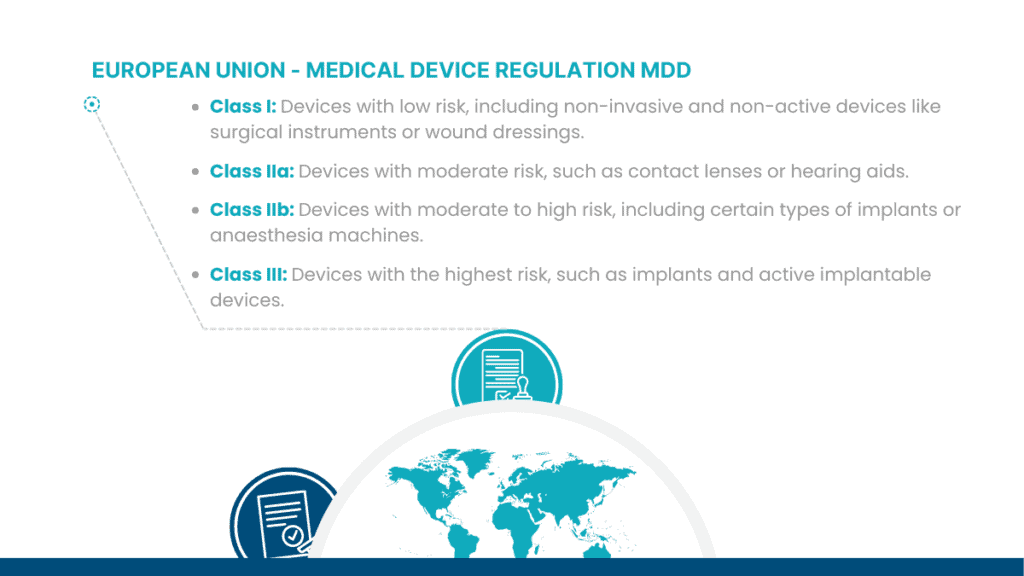
Medical device classification is a regulatory process that categorizes medical devices into different classes based on their intended use, risks, and other relevant factors. The classification system can be a complex landscape, but it helps regulatory authorities establish appropriate regulatory controls and requirements for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical devices.
The classification system may vary depending on the country or region on which you aim to market your medical device; so, the first step is to establish where you intend to market the device.
Below are some examples of commonly used classification systems:
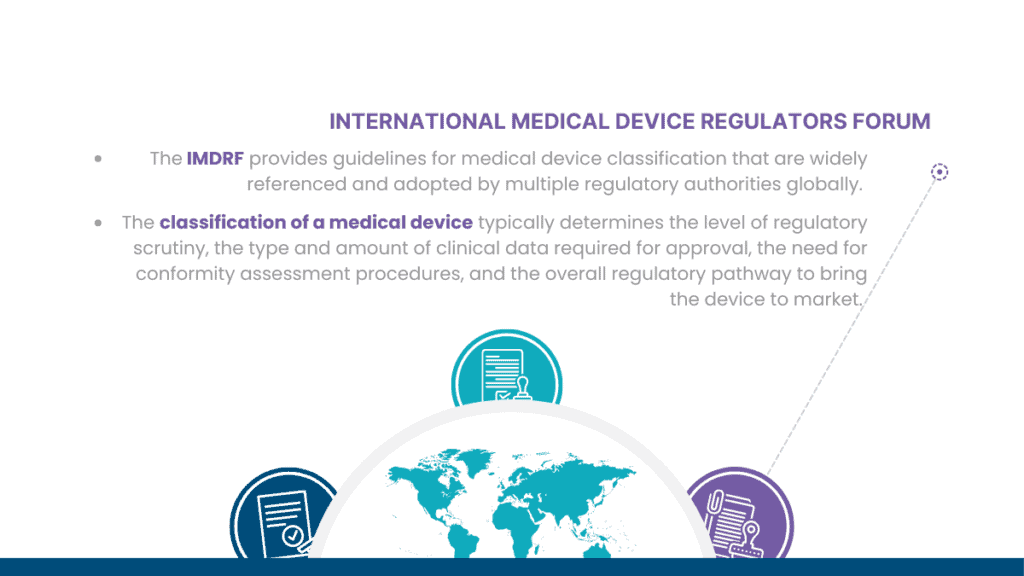
It’s important for medical device manufacturers and designers to understand the classification system in their target market and comply with the applicable regulations to ensure the safety, quality, and effectiveness of their devices.
So, when classifying a medical device, there are several factors that a medical device designer should consider. The classification process helps determine the regulatory requirements and level of scrutiny that the device needs to undergo before it can be marketed. Let’s look at some of the key considerations:
- Intended Use: Clearly define the intended use of the device, this includes identifying the medical purpose, target patient population, and the specific medical conditions or diseases it aims to diagnose, prevent, monitor, treat, or alleviate.
- Risk: Evaluate the potential risks associated with the device. Consider both the severity and probability of harm that the device poses to patients, users, and others. The higher the risks the more stringent regulatory requirements a device will face.
- Duration of Use: Determine whether the device is intended for short-term use i.e. diagnostic tools such as ECG’s & blood pressure monitors, long-term use i.e. continuous glucose monitor, joint movement monitors & Stomas, or permanent implantation such as implants, pacemakers & stents. Implantable devices often have a higher classification due to the potential risks and invasiveness.
- Invasiveness: Consider the degree of invasiveness involved in using the device. Devices that penetrate or interact with the body, such as surgical instruments or implants, typically have higher classifications. Although there are degrees of invasiveness such as under the skin vs implanted devices.
- Ancillary Components: When classifying a device you must consider any additional components, substances, or accessories that are integral to the device’s functioning. These may also impact the device classification.
- Clinical Data and Performance Evaluation: Determine the type and extent of clinical data required to demonstrate the device’s safety and efficacy. Higher-risk devices generally necessitate more extensive clinical investigations and scientific evidence.
WHAT RESOURCES ARE AVAILABLE TO A MEDICAL DEVICE DESIGNER WHEN ESTABLISHING DEVICE CLASSIFICATION?
Although the classification process can be complex, there are resources and experts available that can aid in the process;
EXISTING REGULATORY FRAMEWORK:
Familiarize yourself with the applicable regulatory framework, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classification system, the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR), or other relevant regional or national regulations. Each regulatory body provides guidelines on classifying medical devices based on specific criteria.
CONSULT EXPERTS:
Seek advice from regulatory professionals, clinicians, and experts in the field of medical device classification to ensure a thorough and accurate classification process.

Read More from PolarSeal

Microplate Sealing Films: Selecting the Right Materials and Design
Microplates are essential in laboratory research, allowing for precise tests and analyses that demand meticulous sample handling. An important aspect to ensuring the accuracy of these tests is selecting the right sealing film, which can significantly affect the success of an experiment. Sealing films serve several functions, including preventing evaporation, contamination control and preserving sample integrity. Given the critical nature of these functions, it is important to have a deep understanding of the various types of sealing films available.

Exploring Different Types of Medical Adhesives
Selecting the right adhesive for your medical device is critical for both patient comfort and the profitability of your product. With various types of medical-grade adhesives available, it’s important to understand the unique properties of each to design devices that perform optimally and ensure patient satisfaction. In this blog, we review the different medical-grade adhesives, highlighting the important characteristics and primary use cases of each.

Comparing the Commercial Potential of Healing Agents in Wound Care
The growing demand for healing agents in wound care products offers significant commercial opportunities for medical device companies however it’s crucial to consider the costs, logistics and manufacturing considerations before bringing new products to market. This blog compares various healing agents in wound care to give you a clearer picture of the commercial potential of each.